Prostatitis is an inflammatory disease of the male prostate located below the bladder and is the second part of the genitals.
Every 7 men over 35 have prostatitis, and under the influence of external and internal factors, the risk of each exposure develops an inflammatory process in the prostate.
reason

Inflammation of the prostate may develop for a variety of reasons, and doctors distinguish the main factors:
- The pelvic organs violate blood microcirculation - which leads to a stagnant process and helps increase prostate size. Obesity and sedentary lifestyles promote the stagnation process.
- Bacteria, virus or protozoa in the context of acute or chronic inflammatory processes of other organs flowing in the human body - the kidney, gonorrhea, gonorrhea, urethritis, cystitis, influenza, pyelonephronity can cause disease. If remote areas and organs are infected, the infected pathogenic drugs can enter the prostate and lymph.
- Injury and bruising to soft tissues in the abdomen, perineum and external genitals - this leads to edema and impaired blood circulation in the damaged area;
- Hypothermia.
- Chronic constipation.
- Hormonal diseases.
- Storms or conversely, lack of sex is harmful, preexisting sexual behavior (more than 1 per day), and rare intimacy (less than 1 per week), as this can lead to depletion of the sexual gland or stagnation in the prostate.
Symptoms of prostatitis
Distinguish between acute and chronic forms of the disease.
Acute prostatitis is characterized by a sudden start in the context of a general well, clinically accompanied by the following symptoms:
- chills and weaknesses;
- Generally discomfort;
- Increased irritability and tension;
- Body temperature rises (not higher than 37. 5 degrees);
- Pain in the lower abdomen and perineum;
- While retaining the feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, the urge to urinate frequently;
- The pain of the river and the difficulty of defecation.
In the absence of diagnosis and prompt treatment, acute prostatitis can complicate acute prostatitis during urination and release of pus from the urethra.
Signs of chronic prostatitis
In the chronic form of the disease transitions to this course, the clinical signs of prostatitis and the patient appears to be a recovery. The chronic inflammatory process in the prostate is characterized by burning along the urethra and being irradiated onto the crothra, which can be enhanced during urination and bowel movements. Gradually, the disease progresses and causes yang. Chronic prostatitis means a period of relief and intensification, but even in an intensification moment, the symptoms are eliminated, not as obvious as the acute form. The following symptoms appear clinically:
- Difficulty in getting an erection;
- Unable to complete ejaculation intercourse;
- Reduced sexual desire;
- The urethral mucus excretion of mixed white tablets;
- incomplete empty discharge of the bladder;
- Pain in the lower back, pubic bone and groin pull;
- The urine is weak - this is due to its compressed extended prostate background that narrows the cavity of the urethra.
The chronic inflammatory process in the urethra is irritating to the nerve ends of the pelvis and causes persistent urination, especially at night. Many men are embarrassed to see doctors with such subtle problems, which increases the risk of serious complications such as complete erectile dysfunction, infertility and even prostate cancer.
Furthermore, pathogens focus on chronic infections from the prostate with blood flow and lymph, leading to acute inflammation, urinary retention and increasing the risk of renal failure.
Continuous accumulation of urine in the bladder and urethra is the formation of salt crystals, followed by favorable conditions for stones - often performed simultaneously with prostatitis in men.
Diagnostic method
The diagnosis, treatment and prevention of prostatitis are performed by a urologist. To diagnose and determine the shape and cause of the prostatitis process, many tests were prescribed:
- Palpation of the prostate - Performed through the rectum, allowing you to detect the release of size, pain, pus or mucus after palpation;
- Small emissions from the urethra - sending the final material to the laboratory;
- Urine analysis is general, etc.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and prostate.
If the pathological process is suspected to be transmitted to the patient, the flexible device is equipped with an optical system at the end and the patient's effect is also performed by cystoscopy.
In the diagnosis of prostatitis, it is important to distinguish the pathological process from prostate adenomas and other urological diseases with similar clinical courses.
treat

The treatment of acute and chronic forms of prostatitis is different, so patients are strongly advised not to self-study.
The acute nonbacterial form of prostatitis was fully treated with herbal preparations and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Treatment of acute bacterial prostatitis
The principle of treatment for acute forms of bacterial prostatitis depends directly on the obvious symptoms of the disease.
A unique feature of bacterial prostatitis is an acute onset and rapidly increasing signs of poisoning in the body - nausea, vomiting, headache, high body temperature. The process of emptying the bladder is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen and perineum, which are given to the lower back. The purulent process is often added and the abscess develops.
Treatment of acute bacterial prostatitis is performed in hospitals because the patient's condition can be very serious. Treatment is complex:
- Patients must observe the bed to rest;
- Prescription antibiotics - macrolides, fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins;
- Select preparations that improve blood microcirculation in the pelvic organs. They provide outflow of lymph and venous blood, reducing the severity of edema and inflammatory processes in the prostate.
- Inside the oral administration, a set of drugs with non-replacement anti-inflammatory drugs were shown. These drugs not only reduce the inflammatory process, but also eliminate pain syndrome.
- Pain relief – You can put your tablet in it or introduce a rectal candle into the rectum;
- To eliminate poisoning in the human body, a sodium physiological solution of glucose was registered intravenously.
Important! Prostate massage is strictly prohibited because the risk of sepsis is high.
Surgical treatment
Surgical intervention for prostatitis is only required if the patient's urine is drastically delayed and the bladder is unable to be cleared. Without surgery, a prostate abscess cannot be achieved.
The treatment process for prostatitis lasted for 14 days, after which the patient was again fully examined to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment. If necessary, the treatment process is expanded and adjusted.
Chronic treatment
The treatment of chronic prostatitis depends to a large extent on which stage of the pathological process. If the inflammation process worsens, treatment is also done the same as acute prostatitis.
The treatment of chronic prostatitis during remission is as follows:
- Intake of non-anti-anti-inflammatory drugs. Drugs are 2 times a day at least 3 days, sometimes up to 5 days.
- Preparations that help improve venous and lymphatic efflux.
- Immunomodulator.
- Antidepressants and sedatives help normalize sleep and eliminate irritability.
- Vitamin complex is rich in zinc, selenium, vitamins.
During the remission phase of the prostatitis process, the patient is shown to be treated with physical therapy:
- Prostate massage;
- ultrasound;
- Electrophoresis;
- Magnetic therapy;
- Microwave high temperature.
Surgery treatment for chronic prostatitis
Patients sometimes require surgery due to neglected chronic prostatitis. It can be done in two ways:
- Urethral resection;
- Prostatectomy.
Mental resection
This surgical treatment refers to a minimally invasive intervention, although it is performed under general anesthesia. During this process, a resection mirror is introduced under the urethra and a current pulse is provided. These electrical pulses act on the principle of electrical noise and partially remove the tissue of the prostate. The huge advantage of this intervention is the lack of blood loss, as the radio waves not only eliminate the modified tissue of the prostate, but also treat the blood vessels immediately to prevent bleeding.
Urethral resection significantly promoted the patient's condition - after the surgery, urination resumed, the man no longer burned in his pants, and he would not jump into the toilet at night. Erectile function and normal ejaculation were also restored. The entire operation is controlled by a doctor on the monitor screen, so the risk of complications during operation is very small.
Prostatectomy
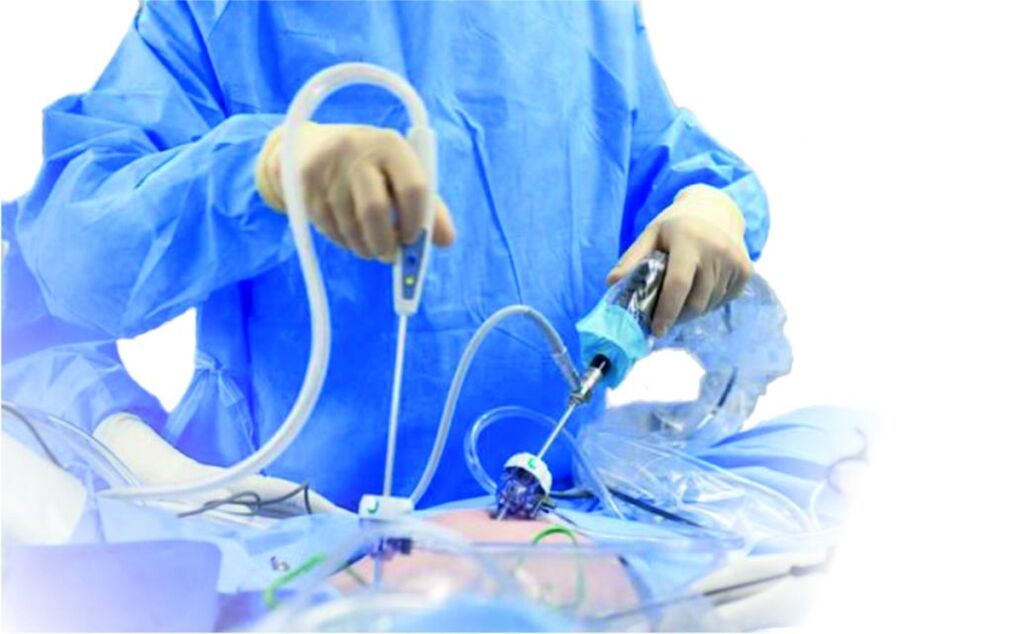
Prostatectomy is a serious abdominal surgery that is always associated with the patient's risk. During the operation, the doctor completely clears the prostate or most of the glands. The recovery period is 4-6 weeks, and there is a high risk of postoperative complications, but sometimes this surgical intervention is the only way to alleviate the patient's condition and eliminate the course of severe prostatitis.
Other ways to treat chronic prostatitis
Other methods for treating chronic prostatitis include:
- Hirudhotherapy-or treatment with water ches. Medical water ches are installed in the inflammatory area. During its action, saliva substances release blood, thereby eliminating stagnation and rapidly alleviating the inflammatory process. Water ech is only used for each patient's special, medical, and individual. After the operation, the doctor placed the used water ech in her death position. Passing at least 5 Hirudotherapy courses is the best choice.
- Cryodstruction - Use liquid nitrogen. This treatment is shown to patients who are undertreated with medication and surgery is contraindicated for some reason.
- Microwave therapy in a special way - electromagnetic waves affect the prostate. After 1 operation, tissue edema was reduced, blood circulation was standardized, and stagnation was eliminated. After the electromagnetic therapy process, the patient fully recovered his urination and erectile function.
- Treat with ultrasound - allows you to quickly stop the inflammatory process that occurs during the relief phase and not perform ultrasound during the aggravation. To enhance the therapeutic effect, a drug can be used separately, which penetrates directly into the tissues of the prostate under the influence of ultrasound.
- Urethral Stent - The essence of this process is to install a special stent in the urethra that enlarges the cavity of the urethra and promotes normal urine outflow. Despite the effectiveness of the surgery, the stents of the urethra only eliminate the clinical symptoms of prostatitis, but do not save the patient from the chronic inflammatory process.
Consequences and complications
In the absence of qualified therapies, prostatitis quickly developed into its current chronic form and threatened a person's health due to its serious complications, including:
- Urolithiasis;
- Pyelonephritis;
- development of abscess;
- The inflammatory process spreads to the testicles and seed ropes, causing infertility.
- Erectile dysfunction and yang ot;
- Necrotic changes in prostate tissue.
Sometimes, prostatitis and chronic stagnation processes drive the disease to degenerate into an adenoma, which then carcinogenizes the prostate.